In the contemporary era, the rising concerns about climate change and the finite nature of traditional energy sources have prompted a global shift towards renewable energy solutions. Solar panels have emerged as a frontrunner in this transition, offering a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional electricity sources. The debate surrounding the economic viability of solar panels compared to the traditional cost of electricity is a pivotal one. This article aims to delve into the intricate details of the solar panel vs. electricity cost dilemma, exploring the economic, environmental, and long-term considerations associated with both options.
Understanding Solar Panel Technology
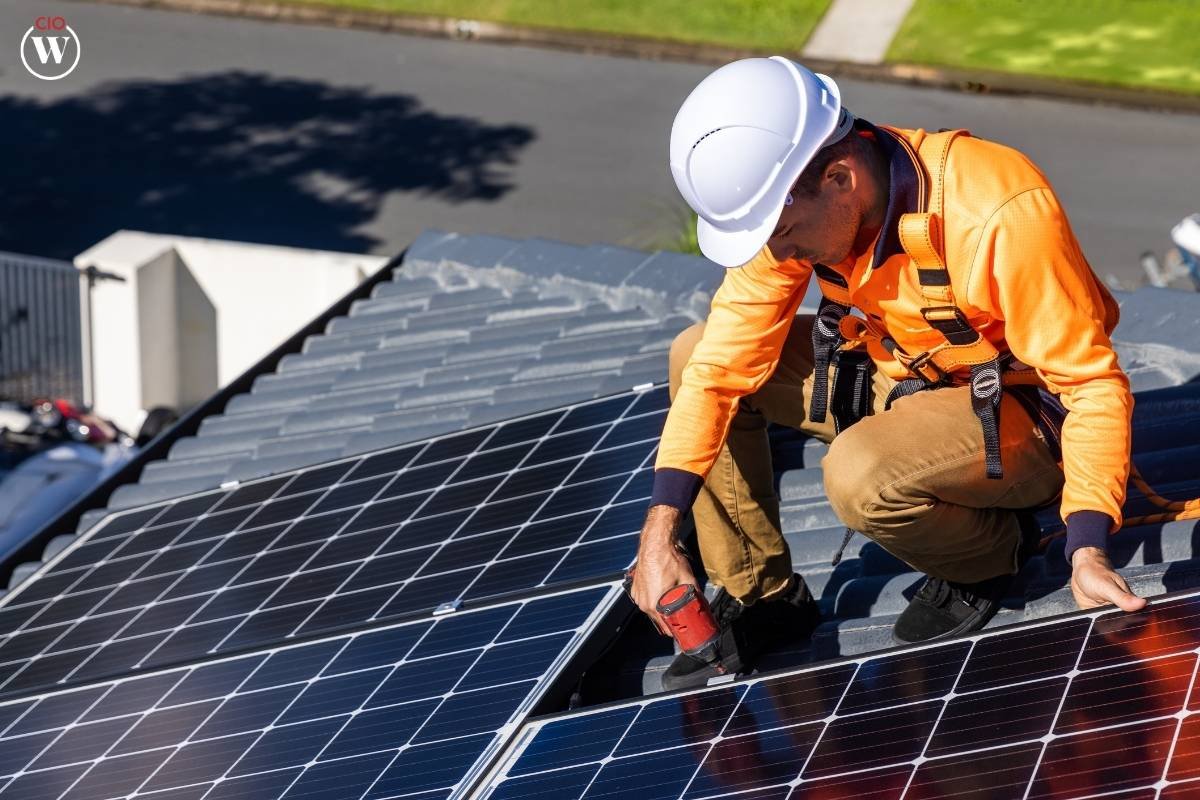

Before delving into the economic aspects, it’s crucial to comprehend the technology that underpins solar panels. Solar panels, also known as photovoltaic (PV) panels, harness sunlight and convert it into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. This process involves the absorption of photons by semiconductor materials within the solar cells, generating an electric current. The electricity produced can then be used to power homes, and businesses, or even feed excess energy back into the grid.
Let’s analyze Solar Panel vs. Electricity Cost
1. The Economic Considerations
One of the primary factors that drive individuals and businesses towards solar panels is the potential for long-term cost savings. Traditional electricity costs are subject to fluctuations based on factors such as fuel prices, geopolitical events, and infrastructure maintenance. On the contrary, solar panels provide a more predictable and stable source of energy once the initial installation costs are covered.
Solar panels require a significant upfront investment, which includes the cost of panels, inverters, mounting systems, and installation. However, advancements in technology and economies of scale have led to a gradual reduction in the upfront costs of solar panel installations. Government incentives, tax credits, and rebates in many regions further contribute to making solar panel installations financially feasible.
Solar panel vs electricity cost comes into play when assessing the long-term savings potential. Solar panels have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years, during which they continue to generate electricity with minimal maintenance costs. In contrast, conventional electricity costs are prone to rise over time due to increasing demand and the need for continuous infrastructure upgrades. We emphasize the constant comparison between solar panel and electricity costs.
2. Environmental Impact
Beyond the economic considerations, the environmental impact is a pivotal aspect of the solar panel vs. electricity cost debate. Traditional electricity generation often relies on fossil fuels, contributing to air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and environmental degradation. In contrast, solar panels generate electricity without emitting harmful pollutants, making them a cleaner and more sustainable option.
The reduction of carbon footprint is a significant advantage associated with solar panels. The use of renewable energy sources aids in mitigating climate change by minimizing dependence on fossil fuels. In this article, we highlight the environmentally conscious choice that solar panels represent in the context of the ongoing climate crisis.
3. Net Metering and Grid Independence
Net metering is a key consideration when evaluating the economic benefits of solar panels. Many regions allow solar panel owners to feed excess electricity back into the grid, effectively running their electricity meters backward. This allows users to earn credits that can be used during periods when their solar panels may not be producing sufficient electricity, such as at night or during cloudy days.

The comparison, solar panel vs. electricity cost, is crucial in discussions about grid independence. Solar panels empower individuals and businesses to reduce their reliance on centralized power grids, offering a degree of energy self-sufficiency. This can be particularly advantageous during power outages or emergencies when grid electricity may be unavailable.
4. Maintenance and Durability
Solar panels are renowned for their low maintenance requirements. Regular cleaning to remove dust and debris is typically sufficient to ensure optimal performance. Additionally, solar panels come with lengthy warranties, further enhancing their cost-effectiveness over their lifespan. The durability and resilience of solar panels contribute to their long-term economic viability, reinforcing the argument for choosing them over conventional electricity sources.
5. Comparing Life Cycle Costs
When comparing solar panel and electricity costs, it’s essential to consider the entire life cycle. This includes the manufacturing, transportation, installation, and eventual disposal of solar panels. While the production of solar panels does have an environmental impact, advancements in manufacturing processes and recycling initiatives have significantly reduced the overall environmental footprint of solar panels.

This article emphasizes the ongoing evaluation and comparison between solar panels and electricity costs throughout their entire life cycle. This holistic approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of the environmental and economic implications associated with each option.
6. Government Incentives and Policy Support
Government incentives and policy support play a crucial role in influencing the economic feasibility of solar panel installations. Many governments around the world offer tax credits, rebates, and other financial incentives to promote the adoption of solar energy. We highlight the importance of government policies in shaping the solar panel vs. electricity cost landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the solar panel vs. electricity cost debate is multifaceted, encompassing economic, environmental, and policy considerations. The debate “solar panel vs electricity cost” serves as a constant reminder of the ongoing evaluation and comparison between these two energy sources.
While the upfront costs of solar panels may pose a barrier, the long-term economic benefits, coupled with the positive environmental impact and government support, make them a compelling choice for individuals and businesses looking to embrace a sustainable and cost-effective energy future. As technology continues to advance and economies of scale drive down costs, the scales may increasingly tip in favor of solar panels as a viable and advantageous alternative to traditional electricity sources.