Mental health stigma is a pervasive issue that has long hindered individuals from seeking the help they need. This stigma has woven itself into the fabric of our society, creating an environment where many suffer in silence, afraid to discuss their mental health concerns openly. In this article, we will explore the concept of mental health stigma, its origins, its consequences, and the steps being taken to break down the barriers to treatment.
Understanding Mental Health Stigma
Mental health stigma refers to the negative attitudes, beliefs, and stereotypes associated with mental illness. It manifests in various ways, from discrimination and exclusion to verbal abuse and the perpetuation of myths and misconceptions about mental health issues. These harmful attitudes and behaviors stem from a lack of understanding and awareness about the nature of mental health disorders.
Mental health stigma often leads to the following consequences:
- Delay in seeking help: Individuals who experience mental health issues may be hesitant to seek treatment due to fear of judgment or discrimination. This delay can exacerbate their condition and make recovery more challenging.
- Isolation: Stigmatized individuals may isolate themselves from friends and family, compounding their feelings of loneliness and despair.
- Negative self-perception: Internalized stigma can lead to low self-esteem and self-worth, making it even more difficult for individuals to reach out for help.
- Barriers to treatment: Stigmatized individuals may face structural barriers such as limited access to quality mental healthcare, insurance discrimination, or difficulties in obtaining appropriate medications and therapies.

The Origins of Mental Health Stigma
Mental health stigma has deep historical roots that have perpetuated its existence in modern society. Several factors have contributed to its development:
- Cultural Beliefs: Cultural norms and beliefs have played a significant role in shaping perceptions of mental health. Some cultures view mental illness as a sign of weakness or moral failure, contributing to stigma.
- Media Portrayals: The media often sensationalizes and stigmatizes mental health issues, perpetuating harmful stereotypes. Fictional depictions of individuals with mental illnesses can reinforce misconceptions and fear.
- Lack of Education: A lack of education and awareness about mental health disorders has allowed stigma to persist. Misinformation and a lack of understanding perpetuate negative attitudes.
- Historical Treatment: In the past, mental health treatment was often inhumane and degrading, contributing to the stigma surrounding it. Institutions that mistreated individuals with mental illnesses left a lasting scar on the perception of mental healthcare.
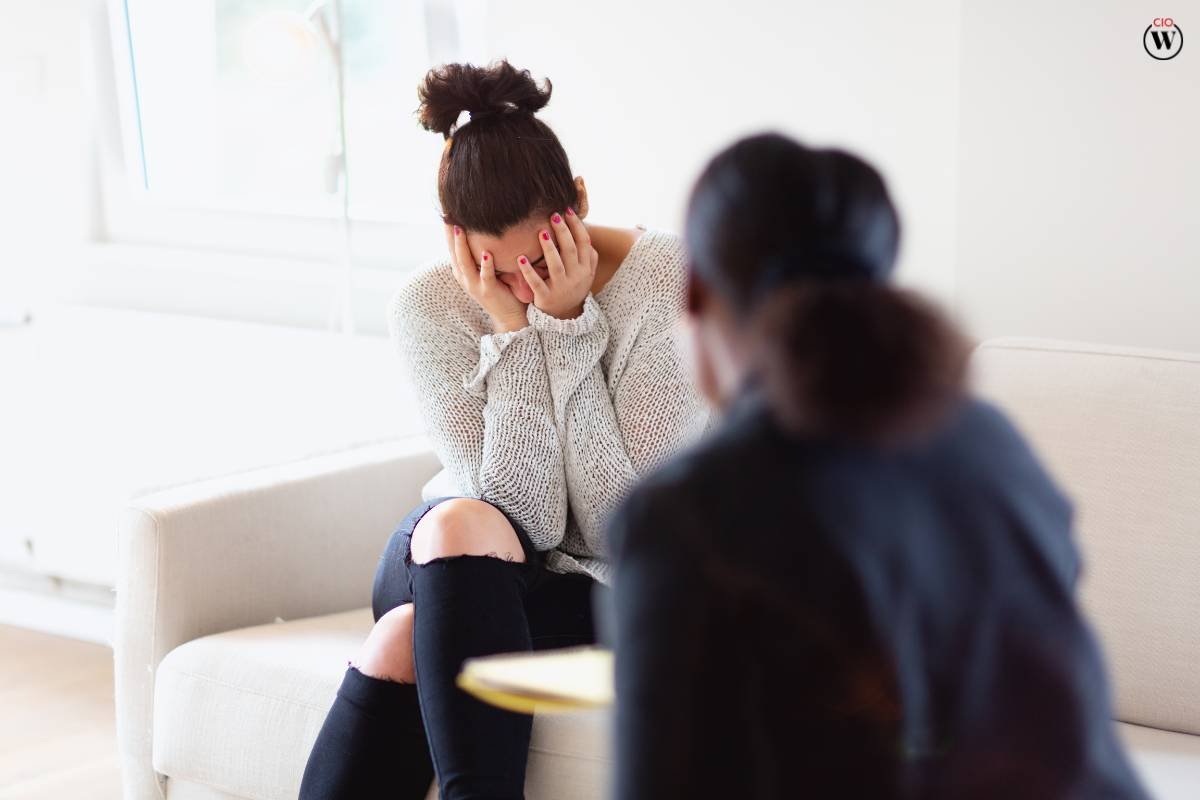

Consequences of Mental Health Stigma
Mental health stigma has far-reaching consequences that affect individuals, families, and society as a whole. Some of the most notable consequences include:
- Underreporting and Misdiagnosis: Stigma can lead individuals to downplay their symptoms, making it difficult for healthcare professionals to accurately diagnose and treat mental health conditions.
- Reduced Access to Treatment: Stigma often deters people from seeking help, which leads to untreated mental health conditions. Without proper treatment, these issues can escalate and cause significant distress.
- Social Isolation: Stigmatized individuals may experience social isolation and discrimination, which can exacerbate their mental health conditions and create a vicious cycle of suffering.
- Employment Discrimination: Stigma can also impact an individual’s professional life. Employees with mental health conditions may face discrimination in the workplace, limiting their career opportunities and financial stability.
- Economic Impact: On a broader scale, mental health stigma can have a significant economic impact. It contributes to lost productivity, increased healthcare costs, and the burden on social services.
Breaking Down Barriers to Treatment
Efforts to combat mental health stigma are crucial for improving the well-being of individuals and society as a whole. Numerous initiatives are making strides in breaking down these barriers to treatment.
- Mental Health Education: Raising awareness and providing accurate information about mental health is fundamental to reducing stigma. Educational programs and campaigns aim to dispel myths and foster understanding.
- Promoting Open Dialogue: Encouraging open conversations about mental health is vital. Public figures, celebrities, and individuals sharing their own mental health struggles can inspire others to seek help.
- Media Responsibility: Advocates are pushing for responsible portrayals of mental health in the media. Accurate depictions of mental illness can help normalize discussions and reduce stereotypes.
- Legislation and Policy Changes: Advocacy for anti-discrimination laws and policies that protect individuals with mental health conditions is essential. These measures can address employment discrimination, insurance disparities, and access to care.
- Access to Quality Care: Improving access to mental healthcare is a critical component of reducing stigma. This includes increasing the number of mental health professionals, reducing wait times, and enhancing the affordability of services.
- Peer Support Programs: Peer support programs connect individuals who have experienced mental health issues with those who are currently struggling. This creates a network of understanding and empathy.
- Crisis Helplines: The establishment of crisis helplines and hotlines provides immediate assistance for those in distress. This can be a lifeline for individuals who may be hesitant to seek treatment.
The Power of Personal Stories

Personal stories of resilience and recovery play a significant role in reducing mental health stigma. When individuals share their experiences with mental health challenges, it helps to normalize these discussions and encourage others to seek help. These stories demonstrate that mental health issues are common and that recovery is possible with appropriate support and treatment.
Conclusion
Mental health stigma remains a formidable barrier to treatment for individuals facing mental health challenges. This stigma can lead to delays in seeking help, isolation, and negative self-perception, with far-reaching consequences for individuals and society. Understanding the origins of stigma and its consequences is the first step in combating it.
Efforts to break down these barriers to treatment are ongoing, with education, advocacy, and policy changes playing crucial roles. By promoting open dialogue, reducing discrimination, and improving access to quality care, we can create a more inclusive and supportive environment for those who are struggling with mental health issues. Ultimately, the power of personal stories and the willingness to listen and empathize can make a profound difference in reducing mental health stigma and ensuring that all individuals have access to the care they need and deserve.
Also read: Ways To Maximize The Happiness And Protection Of Your Family