In the ever-evolving landscape of education, the integration of technology has become paramount to preparing students for the challenges of the 21st century. One of the most exciting and impactful advancements in this realm is the incorporation of robotics in STEM Education (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics Education). This innovative approach not only captivates the imagination of students but also cultivates critical skills essential for success in an increasingly tech-driven world.
The Rise of Robotics in STEM Education
The synergy between robotics and STEM education addresses the growing demand for a workforce with strong technical skills. Robotics provides a hands-on, interactive platform that bridges theoretical knowledge with practical application, making learning more engaging and effective. As the world becomes more reliant on automation and artificial intelligence, fostering a deep understanding of these technologies at an early age is crucial.
- Enhancing Learning through Hands-On Experience
Robotics offers a unique opportunity for students to move beyond traditional classroom settings and actively participate in the learning process. Hands-on experience with robots allows students to apply theoretical concepts in real-world scenarios, reinforcing their understanding of STEM principles. As students build, program, and troubleshoot robots, they develop problem-solving skills, logical reasoning, and a profound sense of accomplishment.
- Fostering Collaboration and Teamwork
Robotics in STEM education often involves collaborative projects that require students to work in teams. This collaborative aspect mirrors the real-world dynamics of scientific and technological endeavors where professionals from diverse backgrounds come together to tackle complex challenges. Students learn not only technical skills but also interpersonal skills such as communication, teamwork, and leadership – attributes that are vital in any professional setting.
- Cultivating Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Skills
Robotics challenges students to think critically and solve problems in real-time. Whether it’s debugging a program, optimizing robot movements, or troubleshooting hardware issues, students are constantly engaged in analytical thinking. These problem-solving skills are transferable to various aspects of life and are particularly valuable in STEM fields where innovative solutions are often required.
- Promoting Creativity and Innovation
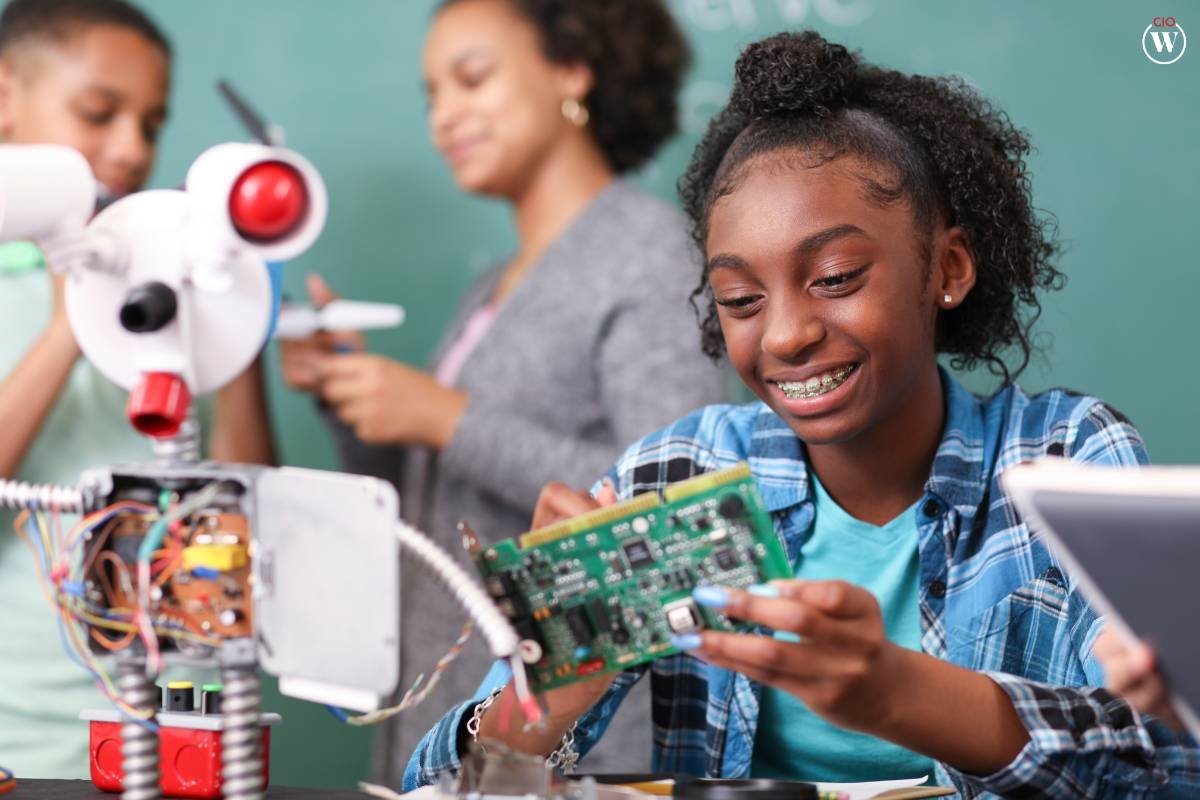

Robotics encourages students to think creatively and innovate as they design and program their robots. The open-ended nature of many robotics projects allows for diverse solutions to a single problem, fostering a culture of creativity. This emphasis on innovation is aligned with the needs of a rapidly changing world, where individuals who can think outside the box and create novel solutions are highly sought after.
- Addressing the Gender Gap in STEM
One notable advantage of introducing robotics in STEM education is its potential to narrow the gender gap in STEM fields. Traditionally, these fields have been male-dominated, but robotics provides an inclusive and inviting space for all students. The hands-on, interactive nature of robotics appeals to a broad range of interests and learning styles, breaking down stereotypes and encouraging more girls to pursue STEM disciplines.
- Challenges and Solutions
While the integration of robotics in STEM education has numerous benefits, it is essential to acknowledge the challenges associated with its implementation. One major hurdle is the cost of acquiring and maintaining robotics kits and equipment. Many schools, especially those with limited resources, may find it challenging to invest in these technologies.
To address this issue, educational institutions can explore partnerships with local industries, seek grants, or leverage community support. Additionally, the availability of affordable and customizable robotics kits has increased, making it more feasible for schools to incorporate robotics into their curriculum.
Another challenge is the need for adequately trained teachers who can guide students in their robotics endeavors. Professional development programs and workshops can equip educators with the necessary skills and knowledge to effectively integrate robotics into their teaching. Collaborations with experts from the industry can also enhance teachers’ understanding of the practical applications of robotics.
Also read: STEM Education For Preschoolers: Everything You Need To Know
Real-World Applications of Robotics in STEM Education
The impact of robotics in STEM education extends beyond the classroom, providing students with valuable exposure to real-world applications of their learning. Here are some examples:
1. Space Exploration and Robotics
Robotics plays a crucial role in space exploration, and students engaged in robotics projects can relate their work to real-life applications in the field. Learning about robotic rovers on Mars or robotic arms on the International Space Station can inspire students to envision exciting career paths in space-related industries.
2. Medical Robotics
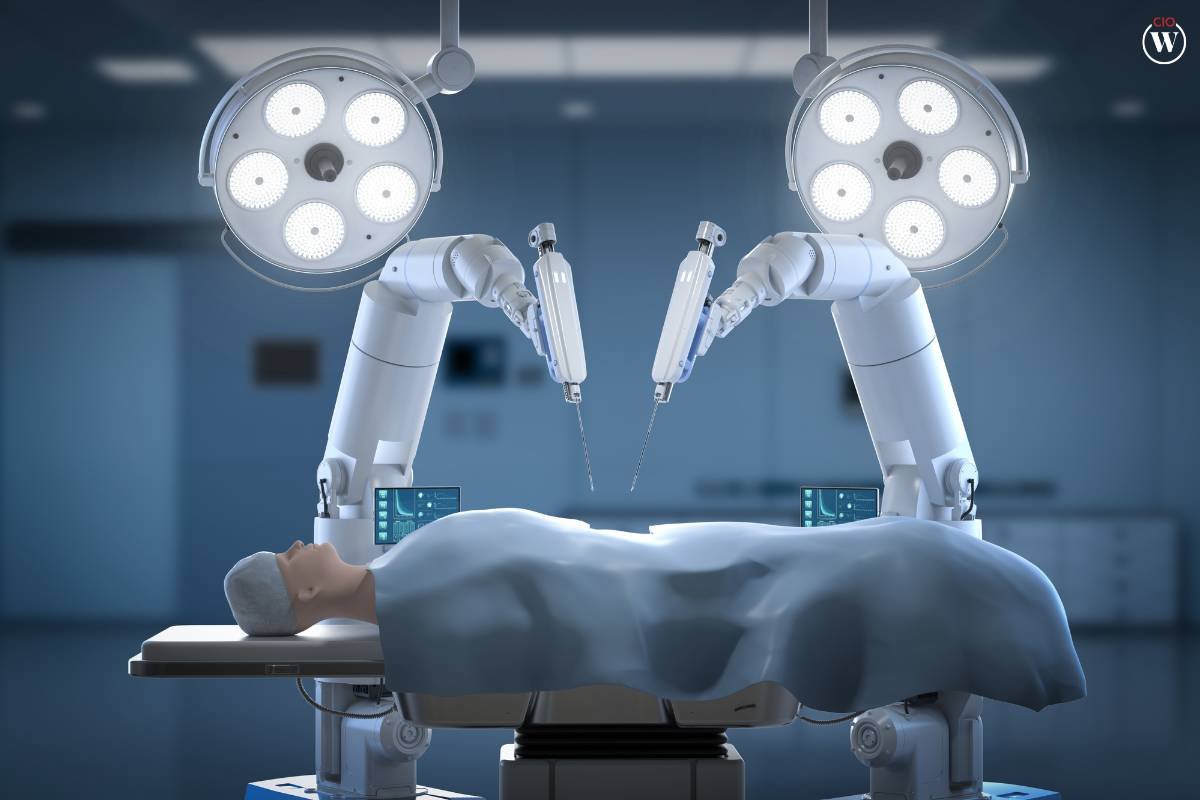
The field of medical robotics is rapidly advancing, with applications ranging from surgical procedures to rehabilitation. Introducing students to medical robotics not only sparks interest but also emphasizes the societal impact of their STEM education. Students can explore the possibilities of designing robots that assist healthcare professionals in various medical tasks.
3. Manufacturing and Automation
Understanding the principles of robotics prepares students for careers in manufacturing and automation. Many industries rely on robotic systems for tasks such as assembly, quality control, and material handling. Exposing students to these applications enhances their awareness of the role robotics plays in streamlining industrial processes.
4. Environmental Monitoring and Robotics
Robotics is instrumental in environmental research and monitoring. Students can engage in projects that involve designing robots for tasks like collecting data on air and water quality, studying ecosystems, or monitoring wildlife. This application connects STEM education with environmental stewardship, instilling a sense of responsibility for the planet.
The Future of Robotics in STEM Education
As technology continues to advance, the role of robotics in STEM education will likely become even more prominent. Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and the Internet of Things are converging with robotics to create new possibilities for learning.
- Integration of AI and Robotics
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into robotics presents exciting opportunities for students to explore the intersection of these fields. AI-powered robots can adapt to changing environments, learn from experience, and perform complex tasks. This integration allows students to delve into cutting-edge technologies and prepares them for the evolving landscape of AI-driven robotics.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality in Robotics Education
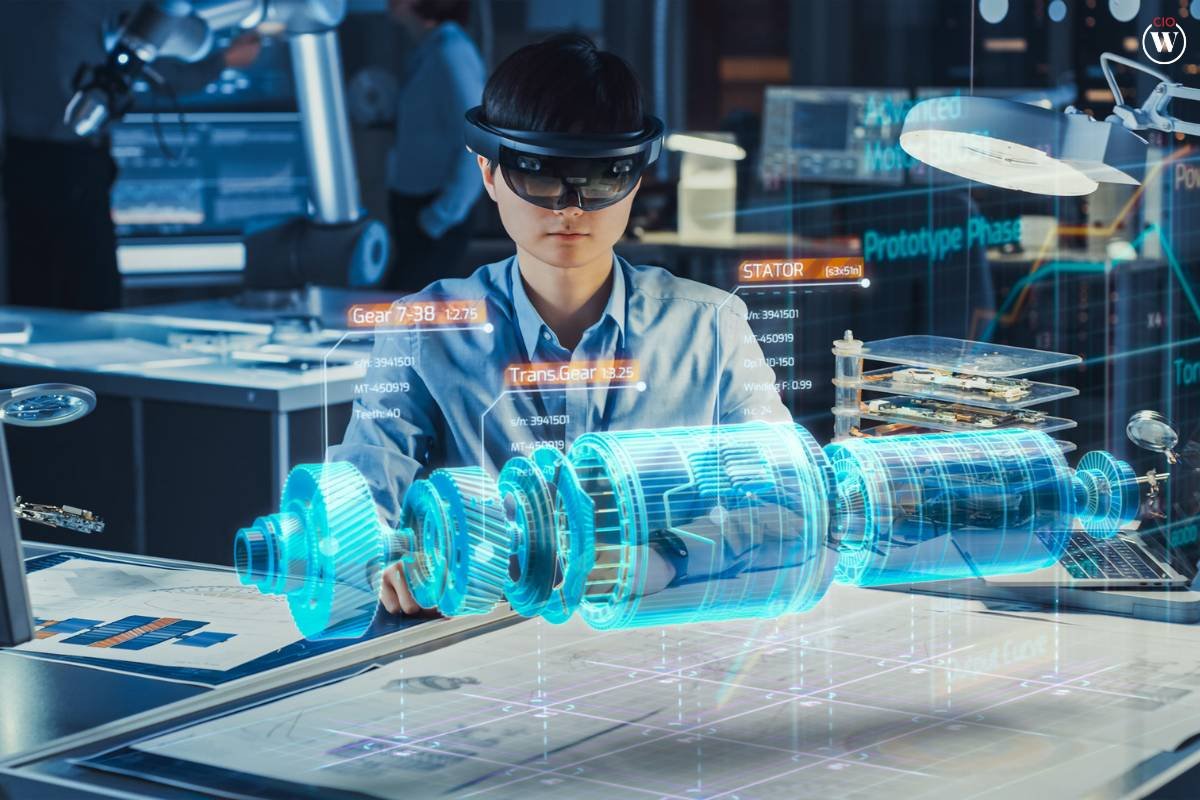

Advancements in virtual and augmented reality (VR/AR) technologies offer immersive experiences in robotics education. Students can engage in virtual simulations, allowing them to test and refine their robotic designs in a digital environment. This not only enhances the learning experience but also provides a cost-effective alternative to physical robotics kits.
- Global Collaboration in Robotics Projects
The interconnected world we live in enables students to collaborate on robotics projects with peers from different parts of the globe. Online platforms and collaborative tools facilitate the sharing of ideas, designs, and solutions. This global perspective enhances students’ understanding of diverse approaches to problem-solving and prepares them for international collaboration in STEM fields.
Conclusion
Robotics in STEM education has emerged as a transformative force, reshaping the way students learn and engage with science and technology. The hands-on, interactive nature of robotics fosters critical skills such as problem-solving, collaboration, and creativity. As we navigate an era defined by rapid technological advancements, preparing students with a solid foundation in STEM education becomes increasingly imperative.
The integration of robotics not only addresses the current needs of the workforce but also cultivates a mindset of lifelong learning and adaptability. By overcoming challenges associated with implementation, fostering inclusivity, and embracing emerging technologies, educators can ensure that robotics remains a cornerstone in shaping the next generation of innovators, scientists, and engineers.
In conclusion, robotics in STEM education is not just a teaching tool; it is a gateway to a future where students are equipped with the skills and mindset needed to thrive in a world driven by technology and innovation.