Remaining healthy entails, a variety of daily behaviors to avoid catching Viral Diseases. Preventing infections is a key part of avoiding both the short-term nuisance of disease and the long-term problems, as well as lowering the danger of transferring infections to those who may be more prone to severe illness.
With the international focus on COVID-19 hazards and prevention, more individuals are taking precautions to prevent virus spread—and the outcomes benefit everyone.
Here are the 7 Best Ways to avoid catching Viral Diseases;
1. Clean your hands
Depending on the climate and pathogen, many pathogenic microorganisms may persist on surfaces for a few minutes to many months (disease-producing microorganisms).
This implies that certain viruses and germs may be able to survive on surfaces you often contact, such as your computer keyboard, light switch, or doorknob.
Hand-to-face and hand-to-mouth transmission are two of the most prevalent methods of infectious illness transmission. Routine handwashing is suggested to prevent pathogen exposure on your lips, eyes, or nose to help decrease this form of dissemination.
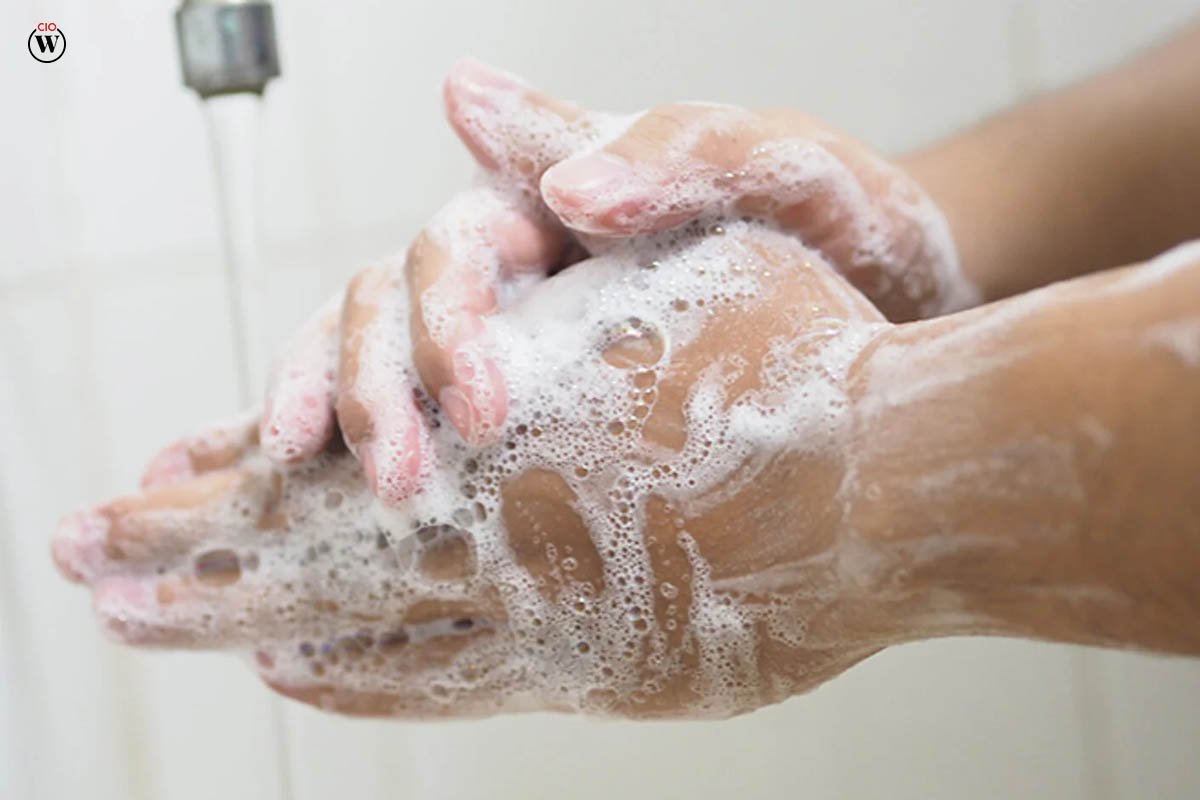

How to Properly Wash Your Hands to avoid catching Viral Diseases
The Centers for avoid catching Viral Diseases and Prevention (CDC) suggests washing your hands thoroughly and vigorously with soap and water for at least 20 seconds—roughly the time it takes to sing “Happy Birthday” twice—and then drying them with a clean towel or air drying.
If you don’t have any water or soap, an alcohol-based hand sanitizer or wipe would suffice.
It’s also a good idea not to pick your nose or bite your nails, particularly if your hands aren’t clean. Teach your children the same.
How to Cleanse Your Hands Correctly?
2. Do not share personal items
Infectious pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites may be found in toothbrushes, towels, razors, handkerchiefs, and nail clippers. These things are known as fomites, which are objects or materials that may transmit illness, such as clothing, kitchenware, or furniture.
Although many viruses have a minimal risk of transmission by fomites, there are a few that might be transferred this way.
Here are some examples to avoid catching Viral Diseases:
It is critical to educate your children not to put toys or things in their mouths and to refrain from doing so yourself (such as chewing on a pencil).
When Your Family Is Sick, How Do You Say Healthy?
3. Cover your mouth
Covering your mouth when you cough or sneeze is an age-old habit of good hygiene.
Droplets may infect persons nearby and transmit several respiratory illnesses. Others are transferred by airborne transmission, in which small aerosol particles may travel large distances in order to infect others.
Upper respiratory tract infections, in which viral or bacterial particles mostly dwell in the nose and throat, provide a greater risk. Coughing may also transmit certain lower respiratory tract illnesses, such as TB.
The CDC suggests covering your mouth with your arm, sleeve, or the crook of your elbow rather than your bare hands to avoid the transmission of respiratory diseases.
4. Get vaccinated
Your immune system is built to remember prior infections, allowing for a quick reaction (in the form of particular antibodies, B cells, or T cells) if the pathogen returns.
Vaccination accomplishes the same function by exposing the body to a weakened or destroyed version of the virus, causing the body to create the same defense cells.
Receiving the necessary vaccines will keep you and those around you safe from infection and sickness. This is a suggested schedule for children, as well as a list of adult immunizations and booster injections (including the annual flu shot).
Put on a Face Mask to avoid catching Viral Diseases
At the commencement of the COVID-19 epidemic, individuals began to use face masks on a daily basis.
Face masks assist you from becoming an infectious respiratory illness and, if you get sick, keep you from infecting others. As a result, wearing a face mask should be practiced in any setting when you have respiratory symptoms and are unable to isolate.
5. Exercise food safety
There are several causes of foodborne disease. This includes gastroenteritis (also known as the stomach flu), a viral illness spread mostly via contaminated food or drink. 10 This includes food poisoning, which may be caused by any of more than 250 different pollutants (including bacteria, viruses, parasites, toxins, and chemicals).
Microbes thrive on almost any meal, especially foods kept at room temperature. Most bacteria may be slowed or stopped in their development if they are refrigerated within two hours after being prepared.
Also, utilizing two cutting boards—one for raw meats and one for produce—can help to reduce cross-contamination. Keep your counters clean, wash your hands often, and wash any raw fruits and vegetables before eating.
If your immune system is impaired (you have a lower capacity to fight infections), you may need to take a step further by cooking meats until thoroughly done and peeling or scraping all vegetables and fruits. This precaution is particularly important for pregnant women, the elderly, and small children, who are more vulnerable to food poisoning.
6. Be safe when traveling
Infectious infections are often acquired when traveling, especially in resource-limited nations.
You may lower your risk by doing the following:
Use bottled water for drinking and brushing your teeth if the water quality at your location is uncertain. You should also avoid using ice cubes, which might be contaminated.
Avoid eating raw or undercooked meat, poultry, or fish: Only consume these things after they are completely cooked to avoid catching Viral Diseases.
Vegetable and fruit preparation: When eating fruit, pick those that can be peeled and make sure the skin does not come into touch with the remainder of the fruit during peeling.
Next, ensure that you are up to date on any vaccines that are required or recommended for those going to your locations. You may find them on the CDC’s Travelers’ Health website.
The CDC’s website also provides up-to-date travel warnings concerning outbreaks and other health problems (both domestic and international), as well as recommendations about food-borne illness outbreaks.
If you have a damaged immune system, see your doctor before going since some immunizations (such as the yellow fever vaccine) may not be safe for you.
7. Stay away from animal-borne diseases
Diseases that may be transmitted from animals to humans, known as zoonotic illnesses, are more frequent than many people assume. If you have pets, make sure they receive regular exams and are up to date on their vaccines to avoid catching Viral Diseases. Keep tiny children away from animal waste and clean litter boxes on a regular basis. If you are pregnant or immunocompromised, have someone else clean the litter box since cat excrement is a common source of toxoplasmosis and cytomegalovirus (CMV).

Wild animals may also transmit diseases like rabies, avian flu, and flea or tick-borne illnesses like Lyme disease. To help avoid catching Viral Diseases, make your house unwelcoming to rats by removing spots where they may hide or develop nests. To prevent attracting wildlife, use animal-proof garbage cans and educate young children that wild creatures should never be approached or handled.









