Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) affects millions of women worldwide, impacting their reproductive health, hormonal balance, and overall well-being. Managing PCOS requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating lifestyle changes, medication, and sometimes medical interventions. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the intricacies of PCOS management, offering practical advice and insights to empower women in their journey towards better health and quality of life.
Understanding PCOS: Unraveling the Complexity
Before diving into management strategies, it’s crucial to grasp the fundamentals of PCOS. Characterized by hormonal imbalances and enlarged ovaries containing multiple small cysts, PCOS manifests differently in each individual. Common symptoms include irregular menstrual cycles, excessive hair growth, acne, weight gain, and fertility issues. However, not all women with PCOS experience the same symptoms or severity, making diagnosis and treatment challenging.
1. Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis forms the cornerstone of effective PCOS management. If you suspect you may have PCOS, consult a healthcare provider experienced in reproductive endocrinology. Diagnosis typically involves a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, blood tests to assess hormone levels, and imaging studies such as ultrasound to evaluate ovarian morphology.

Early detection enables timely intervention, minimizing the risk of long-term complications such as infertility, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and endometrial cancer. Additionally, ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms is crucial to tailor treatment plans effectively.
2. Lifestyle Modifications: Nurturing a Healthy Foundation
Implementing lifestyle modifications plays a pivotal role in managing PCOS and mitigating its symptoms. These adjustments aim to improve insulin sensitivity, regulate hormones, promote weight loss, and enhance overall well-being. Key lifestyle interventions include:
- Balanced Diet:
Adopting a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats can help stabilize blood sugar levels and manage weight. Emphasize low-glycemic index foods to prevent spikes in insulin, a hormone linked to PCOS symptoms.
- Regular Exercise:
Engaging in regular physical activity not only aids in weight management but also enhances insulin sensitivity and promotes hormone balance. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, incorporating both cardiovascular and strength-training exercises.
- Stress Management:
Chronic stress can exacerbate PCOS symptoms by elevating cortisol levels and disrupting hormonal equilibrium. Practice stress-reducing techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing exercises, and mindfulness to foster emotional well-being and hormonal harmony.
- Adequate Sleep:
Prioritize quality sleep to support hormone regulation, metabolism, and overall health. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep each night, maintaining consistent sleep-wake schedules to optimize hormonal balance.
3. Medication and Hormonal Therapy
In addition to lifestyle modifications, pharmacological interventions may be necessary to manage specific symptoms and underlying hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS. Common medications prescribed for PCOS management include:
- Oral Contraceptives:
Birth control pills containing estrogen and progestin can regulate menstrual cycles, reduce androgen levels, and alleviate symptoms such as acne and hirsutism (excessive hair growth).
- Anti-Androgen Medications:
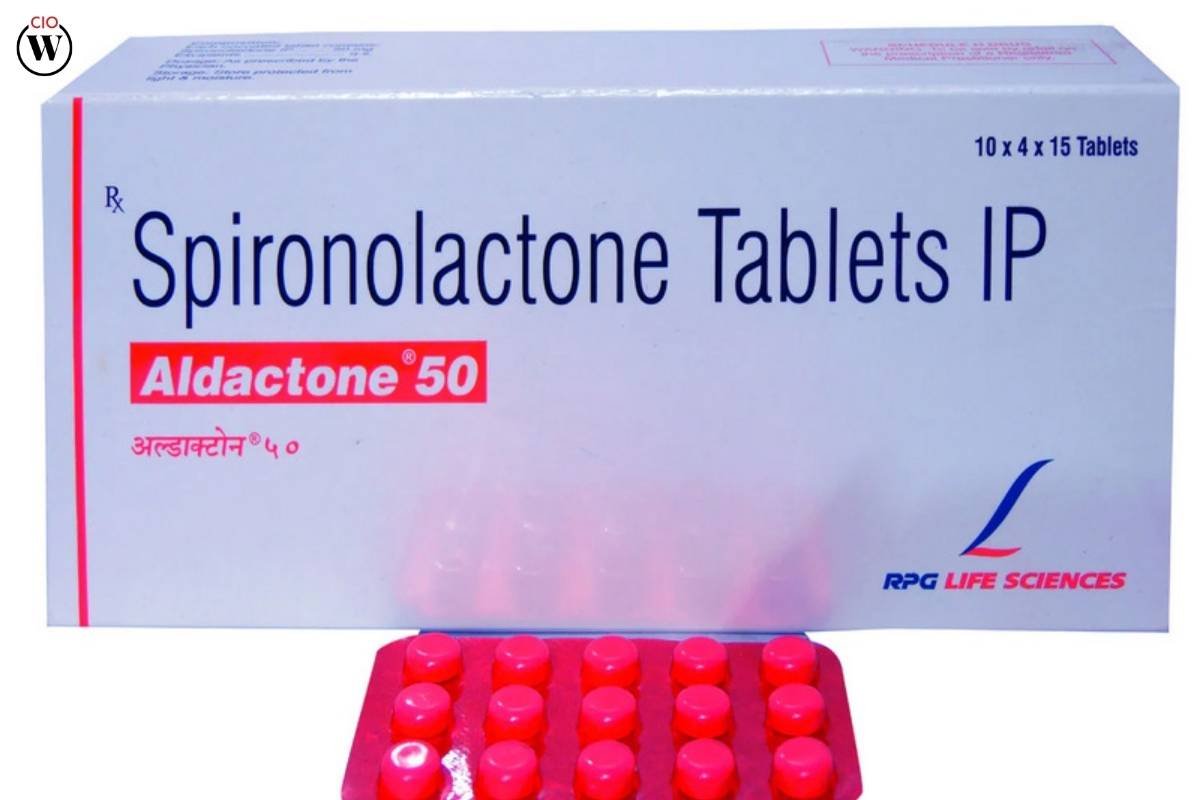
Drugs like spironolactone can block the effects of androgens, reducing symptoms such as acne, hirsutism, and male-pattern baldness.
- Metformin:
Originally used to treat type 2 diabetes, metformin is also effective in improving insulin sensitivity and regulating menstrual cycles in women with PCOS. It may be prescribed alone or in combination with other medications.
- Ovulation Induction:
Women seeking to conceive may benefit from medications such as clomiphene citrate or letrozole to induce ovulation and improve fertility.
- Hormonal Therapy:
In cases of infertility or persistent hormonal imbalances, hormone therapy with medications like gonadotropins or GnRH analogs may be recommended to stimulate ovulation or regulate menstrual cycles.
4. Dietary Supplements and Herbal Remedies
Complementary therapies, including dietary supplements and herbal remedies, are often used adjunctively to manage PCOS symptoms and promote hormonal balance. While research on their efficacy is ongoing, some supplements may offer potential benefits:
- Inositol:
A naturally occurring compound, inositol, particularly myo-inositol and D-chiro-inositol, has shown promise in improving insulin sensitivity, ovarian function, and menstrual regularity in women with PCOS.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids:
Omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oil may help reduce inflammation, lower androgen levels, and improve lipid profiles in women with PCOS.
- Vitamin D:
Deficiency in vitamin D is common among women with PCOS and may exacerbate symptoms. Supplementation with vitamin D has been associated with improved menstrual regularity and insulin sensitivity.
- Herbal Remedies:
Herbs such as cinnamon, spearmint, and licorice root are purported to have anti-androgenic or insulin-sensitizing effects, though evidence supporting their efficacy in PCOS management is limited.
5. Surgical Interventions: Exploring Options
In select cases where medical and lifestyle interventions fail to achieve desired outcomes, surgical interventions may be considered to address specific concerns associated with PCOS:
- Ovarian Drilling:
A minimally invasive surgical procedure, ovarian drilling involves using heat or laser to puncture the ovarian cysts, potentially reducing androgen production and restoring ovulation in women with PCOS.
- Bariatric Surgery:
For women with severe obesity and PCOS-related metabolic complications, bariatric surgery may be an option to achieve substantial weight loss, improve insulin sensitivity, and alleviate symptoms.
- Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART):
In cases of infertility related to PCOS, assisted reproductive techniques such as in vitro fertilization (IVF) or intrauterine insemination (IUI) may be employed to facilitate conception.
Empowering Women through Knowledge and Support
Managing PCOS is an ongoing journey that requires patience, persistence, and a proactive approach. By understanding the condition, implementing lifestyle modifications, adhering to prescribed medications, and seeking appropriate medical care, women with PCOS can effectively manage their symptoms, optimize fertility, and safeguard their long-term health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing PCOS involves a multifaceted approach encompassing lifestyle modifications, medication, and sometimes surgical interventions. By addressing hormonal imbalances, insulin resistance, and associated symptoms, women with PCOS can take control of their health and well-being. Through education, advocacy, and support, individuals affected by PCOS can navigate their journey with confidence, resilience, and hope for a brighter future.
Also read: Health Care Tips Every Woman Needs to Follow to Stay Healthy