In the bustling heart of cities, amidst towering skyscrapers and busy streets, a quiet revolution is taking root – urban farming. As urbanization continues to accelerate worldwide, the concept of growing food within city limits is gaining momentum as a sustainable solution to food insecurity, environmental degradation, and disconnected communities. In this article, we delve into the world of urban farming, exploring its benefits, challenges, and the promising future it holds.
What is Urban Farming?
Urban farming, also known as urban agriculture or urban gardening, refers to the practice of cultivating, processing, and distributing food in urban areas. It encompasses a wide range of techniques, from rooftop gardens and vertical farms to community gardens and aquaponics systems. Farming aims to utilize underutilized spaces within cities to produce fresh, nutritious food for local consumption.
The Benefits of Urban Farming
1. Food Security
One of the primary benefits of urban farming is its potential to enhance food security in densely populated areas. By growing food locally, urban farmers reduce reliance on long-distance food transportation networks, thereby decreasing the risk of supply chain disruptions due to factors such as extreme weather events or transportation issues.
2. Environmental Sustainability
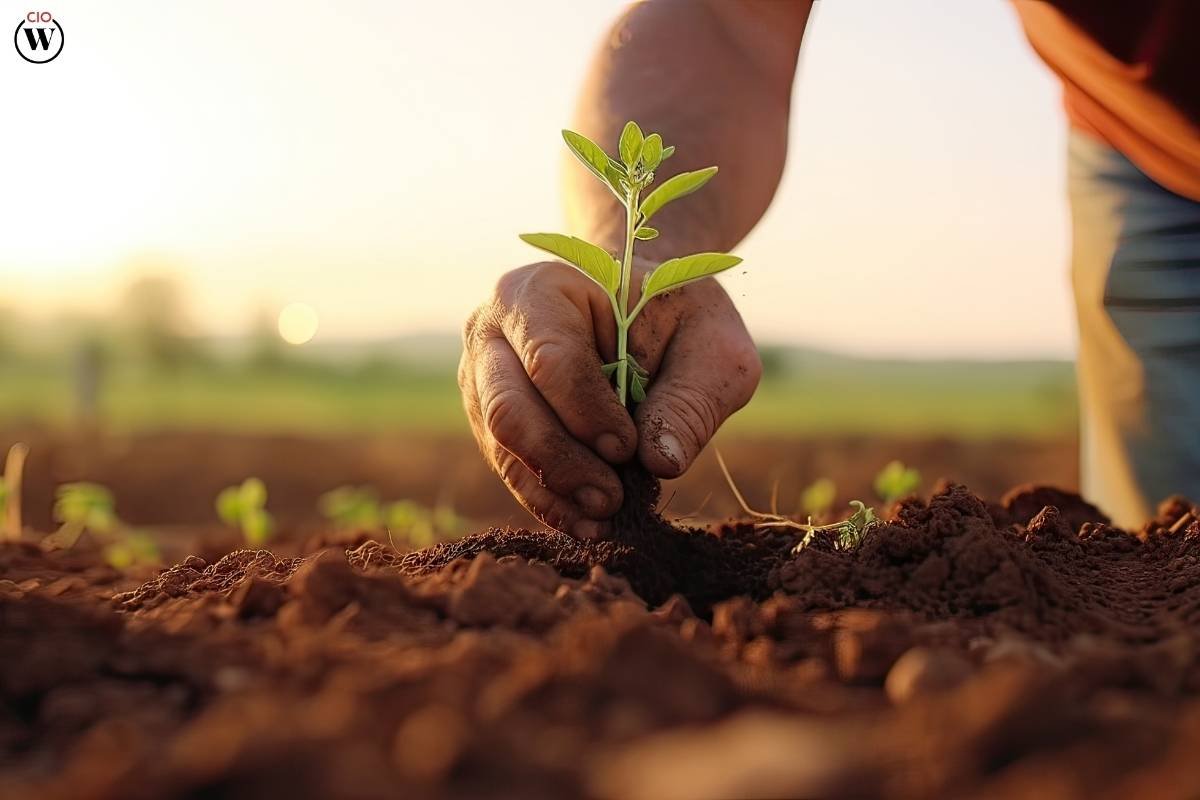

Urban agriculture promotes environmental sustainability by reducing the carbon footprint associated with conventional agriculture. By minimizing transportation distances, urban farmers decrease greenhouse gas emissions generated during the transportation and distribution of food. Additionally, practices such as composting organic waste and utilizing rainwater harvesting techniques contribute to the conservation of natural resources.
3. Community Engagement
Urban farming fosters community engagement by bringing people together around a shared interest in food production and environmental stewardship. Community gardens serve as gathering spaces where residents can socialize, share knowledge, and collaborate on gardening projects. These spaces promote a sense of belonging and connection among diverse urban populations, strengthening social bonds and enhancing community resilience.
Challenges Facing Urban Farming
While urban farming offers numerous benefits, it also faces several challenges that must be addressed to realize its full potential.
1. Land Availability and Access
One of the primary challenges for urban farmers is securing suitable land for cultivation. In densely populated cities, available land is often limited and expensive, making it difficult for aspiring urban farmers to establish or expand their operations. Additionally, zoning regulations and land-use policies may pose barriers to the development of urban farming initiatives.
2. Resource Constraints
Urban agriculture requires access to essential resources such as water, sunlight, and soil. In urban environments, these resources may be limited or of poor quality, posing challenges for successful crop production. Innovative solutions such as hydroponics, aquaponics, and vertical farming can help overcome resource constraints by utilizing alternative growing methods that require fewer inputs.
3. Economic Viability

Achieving economic viability is another challenge for urban farmers, particularly small-scale operators. High land and operating costs, combined with competitive pricing from conventional agriculture, can make it difficult for urban farmers to generate sufficient revenue to sustain their operations. To address this challenge, urban farmers may need to explore alternative revenue streams such as value-added products, agritourism, or direct-to-consumer sales through farmers’ markets or community-supported agriculture (CSA) programs.
The Future of Urban Farming
Despite the challenges, the future of urban farming appears promising, driven by growing awareness of the importance of sustainable food systems and the potential of innovative technologies. As urban populations continue to expand, the demand for locally grown, fresh produce is expected to rise, creating opportunities for urban farmers to thrive.
1. Technological Innovations
Advancements in technology are transforming the landscape of urban farming, making it more efficient, productive, and sustainable. From automated vertical farming systems equipped with LED lighting and hydroponic nutrient delivery systems to smartphone apps that monitor crop health and environmental conditions, technology is revolutionizing the way food is grown in cities.
2. Policy Support

Governments and policymakers are increasingly recognizing the value of urban farming as a means to promote food security, environmental sustainability, and community development. By implementing supportive policies such as urban agriculture zoning ordinances, land-use incentives, and funding programs for urban farming initiatives, policymakers can create an enabling environment for the growth of urban agriculture.
3. Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness about the benefits of urban farming and providing education and training opportunities for aspiring urban farmers are critical steps in ensuring the long-term success of urban farming initiatives. By engaging with local communities through outreach programs, workshops, and educational events, urban farmers can inspire more people to get involved in food production and contribute to a more sustainable future.
Conclusion
Urban farming holds immense promise as a sustainable solution to the challenges of food insecurity, environmental degradation, and disconnected communities in urban areas. By harnessing the power of nature in the concrete jungle, urban farmers are transforming cities into vibrant, resilient, and self-sufficient hubs of food production. With continued support from policymakers, technological innovation, and community engagement, urban farming has the potential to play a significant role in building a more sustainable and equitable food system for future generations. Embracing the principles of urban farming today can pave the way for a healthier, greener, and more prosperous tomorrow.